Ozempic, Semaglutide, and GLP-1 Medications: Full Guide for Weight Loss & Health
Trimmed&Toned Team.
Ozempic, Semaglutide, and GLP-1 Medications: A Complete Fitness Guide
If you’ve opened a health article, scrolled through social media, or even overheard a conversation in a coffee shop this year, chances are you’ve heard about Ozempic. This injectable medication — along with other drugs in the same class like Wegovy and Mounjaro — has become a cultural phenomenon. Some people hail it as a “miracle” weight loss solution, while others warn about side effects and long-term consequences. The truth, as with most things in health and fitness, lies somewhere in the middle.
At our core, we believe that the best foundation for weight management comes from healthy eating, regular exercise, good sleep, and sustainable habits. But we also recognize that Ozempic and other GLP-1 medications are part of today’s weight-loss landscape, and people deserve clear, compassionate, and accurate information. In this guide, we’ll cover what Ozempic is, how it works, why people use it, potential risks, how it’s administered, and most importantly, how it fits into a bigger picture of health.
What Exactly Is Ozempic (Semaglutide)?
Ozempic is the brand name for semaglutide, a type of drug called a GLP-1 receptor agonist. GLP-1 stands for glucagon-like peptide-1, a hormone your body naturally produces in the gut after eating. This hormone helps regulate blood sugar, slows digestion, and tells your brain you’re full. In simple terms: it helps control appetite and keeps blood sugar steady.

Semaglutide was first approved to treat type 2 diabetes, because it improves insulin sensitivity and lowers blood sugar levels (Mayo Clinic). But doctors and researchers quickly noticed that patients were losing weight — sometimes a significant amount. This led to further studies, and eventually, semaglutide was also approved for weight management under the brand name Wegovy.
How Does Ozempic Help With Weight Loss?
The way Ozempic helps with weight loss comes down to three main effects:
- Appetite suppression: Ozempic makes you feel full sooner and for longer. People often report they’re simply not as interested in food as before.
- Slower digestion: It delays how quickly food leaves your stomach, which extends feelings of satiety (fullness).
- Blood sugar control: Stable blood sugar means fewer spikes and crashes, which reduces cravings for sugary, high-calorie foods.
Combined, these effects can lead to significant reductions in calorie intake without the same level of hunger and cravings that often sabotage diets. That’s why so many people are curious about Ozempic weight loss results and whether it could work for them.
How Is Ozempic Administered?
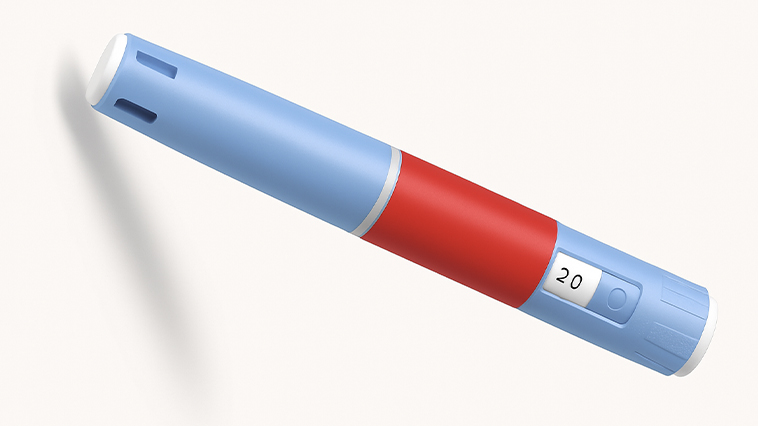
One of the most common questions people ask is: how do you take Ozempic?
Ozempic is not a pill. It’s administered as a once-weekly injection using a pre-filled pen. Most people inject it into the stomach, thigh, or upper arm. The pen is designed to be relatively simple to use, and doctors or nurses usually teach patients how to self-administer at home.
The dosage typically starts low (0.25 mg) to minimize side effects, and then gradually increases over several weeks until the maintenance dose is reached. This slow titration is important — jumping in too quickly can lead to nausea, vomiting, or gastrointestinal issues.
What Are the Benefits of Ozempic for Weight Loss?
Studies have shown that Ozempic and other semaglutide-based medications can help patients lose an average of 10–15% of their body weight, with some experiencing even more significant reductions (NEJM).
Some of the main reported benefits include:
- Substantial weight loss: Often more than traditional diet and exercise alone.
- Better blood sugar control: Particularly important for people with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
- Improved heart health markers: Some studies show lower blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Increased confidence: For many, losing weight boosts mood and motivation to maintain healthier habits.
It’s important to note, however, that the benefits are usually maintained only while continuing the medication. Once people stop, weight regain is common.
What Are the Side Effects of Ozempic?
While the benefits can be impressive, Ozempic also comes with potential side effects. The most common are related to the digestive system:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Stomach pain or bloating
These side effects are often worse at the beginning of treatment or after a dose increase, and they sometimes improve over time. However, there are also more serious (but rarer) risks, such as:
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, which can be very serious.
- Gallbladder issues: Gallstones or gallbladder inflammation.
- Possible thyroid tumors: In animal studies, semaglutide has been linked to thyroid tumors, though the risk in humans isn’t fully clear (FDA).
For this reason, Ozempic is not recommended for people with a personal or family history of certain thyroid cancers.
Who Is Ozempic For?
Doctors generally prescribe Ozempic or other GLP-1 medications for:
- People with type 2 diabetes who need help controlling blood sugar.
- Adults with a BMI over 30 (classified as obese).
- Adults with a BMI over 27 who also have weight-related health conditions, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or sleep apnea.
For people outside these categories, lifestyle approaches — such as intermittent fasting or high-protein diets — are usually recommended before medication.
What Happens If You Stop Taking Ozempic?
This is one of the biggest questions surrounding Ozempic: what happens when you stop taking it?
Research shows that many people regain a significant portion of the weight they lost once they stop semaglutide. This is because the appetite suppression and slower digestion go away, and the body’s natural hunger signals return. If someone hasn’t built sustainable eating and exercise habits while on the medication, it’s very easy to slip back into old patterns.
This is why experts emphasize: Ozempic is not a cure. It’s a tool. It works best when combined with lifestyle changes that can carry you forward even if you eventually stop the medication.

Natural Alternatives to Ozempic
While there isn’t a natural food or supplement that works exactly like semaglutide, several strategies can mimic its appetite-suppressing and blood-sugar-stabilizing effects:
- High-protein meals: Protein is the most satiating macronutrient and helps control hunger naturally.
- Fiber-rich foods: Vegetables, beans, and whole grains slow digestion and extend fullness.
- Mindful eating: Paying attention to hunger cues helps prevent overeating.
- Regular exercise: Especially strength training, which improves insulin sensitivity and boosts metabolism.
- Sleep and stress management: Poor sleep and high stress can disrupt hunger hormones like ghrelin and leptin, making cravings stronger.
We dive deeper into this in our article on natural appetite suppressants that really work.
FAQs About Ozempic and Weight Loss
- Is Ozempic safe without diabetes?
Yes, in many places it’s approved for obesity management, but always under medical supervision. - How long can you stay on Ozempic?
Some people use it long-term, but ongoing medical monitoring is required. It isn’t meant to be used casually or for cosmetic weight loss alone. - Can you drink alcohol on Ozempic?
Moderate drinking may be allowed, but alcohol can worsen nausea and interfere with blood sugar control. - Does Ozempic give energy?
Indirectly, weight loss and better blood sugar stability can improve energy levels, but Ozempic itself isn’t a stimulant. - Is Ozempic better than diet and exercise?
It can accelerate weight loss, but diet and exercise are still the foundation for long-term success. - Can Ozempic replace healthy habits?
No. Think of it as scaffolding — it supports weight loss, but the permanent structure is built with nutrition, training, and lifestyle choices.
Final Thoughts
Ozempic and other GLP-1 medications have changed the conversation about weight loss. For people with serious health conditions or those who have struggled for years without success, these medications can be life-changing. But they aren’t without drawbacks, and they certainly aren’t a replacement for building strong, sustainable habits.
If you’re considering Ozempic, the best step you can take is to talk to a healthcare provider, weigh the risks and benefits, and think about how it fits into your bigger picture of health. Whether you use medication or not, the cornerstones of long-term weight management remain the same: balanced eating, consistent exercise, good sleep, and daily practices that support your well-being.
Quick fixes may come and go, but true health is built step by step, habit by habit.
Medical Reminder: Always consult your doctor or healthcare provider before making major changes to your eating habits, exercise routine, or lifestyle. This article is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Trimmed&Toned Team.